
Almost every portable and handheld device consist a battery. The battery is a storage device where energy is stored to provide the power whenever needed. There are different types of batteries available in this modern electronics world, among them Lead Acid battery is commonly used for high power supply. Usually Lead Acid batteries are bigger in size with hard and heavy construction, they can store high amount of energy and generally used in automobiles and inverters.
Even after getting competition with Li-ion batteries, Lead acid batteries demand is increasing day by day, because they are cheaper and easy-to-handle in comparison with Li-ion batteries. As per some market research India Lead Acid Battery Market is projected to grow at CAGR of over 9% during 2018-24. So, it has huge market demand in Automation, Automotive, and Consumer Electronics. Altough most of the Electric vehicle comes with Lithion-ion batteries, but still there are many electric two wheeler which use Lead Acid battries to power the vehicle.
In previous tutorial we learned about Lithium-ion batteries, here we will understand the Working, construction and applications of Lead Acid Batteries. We will also learn about charging/discharging ratings, requirements and safety of Lead Acid Batteries.
Construction of Lead Acid Battery
What is a Lead Acid Battery? If we break the name Lead Acid battery we will get Lead, Acid, and Battery. Lead is a chemical element (symbol is Pb and the atomic number is 82). It is a soft and malleable element. We know what Acid is; it can donate a proton or accept an electron pair when it is reacting. So, a battery, which consists of Lead and anhydrous plumbic acid (sometimes wrongly called as lead peroxide), is called as Lead Acid Battery.
Now, what is the internal construction?
A Lead Acid Battery consists of the following things, we can see it in the below image:
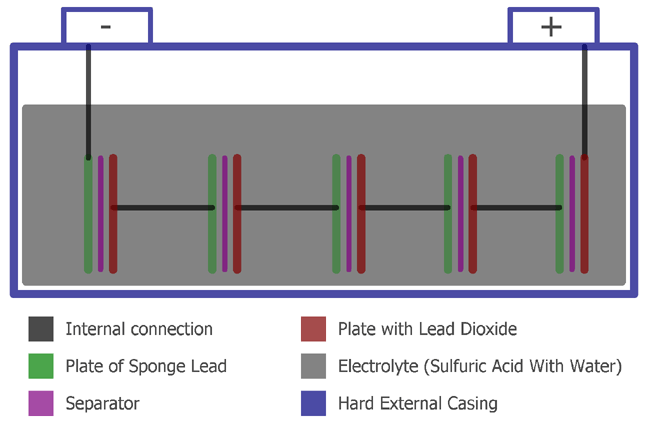
A Lead Acid Battery consists of Plates, Separator, and Electrolyte, Hard Plastic with a hard rubber case.
In the batteries, the plates are of two types, positive and negative. The positive one consists of Lead dioxide and negative one consists of Sponge Lead. These two plates are separated using a separator which is an insulating material. This total construction is kept in a hard plastic case with an electrolyte. The electrolyte is water and sulfuric acid.
The hard plastic case is one cell. A single cell store typically 2.1V. Due to this reason, A 12V lead acid battery consists of 6 cells and provide 6 x 2.1V/Cell = 12.6V typically.
Now, what is the charge storage capacity?
It is highly dependable on the active material (Electrolyte quantity) and the plate’s size. You may have seen that lithium battery storage capacity is described in mAh or milliamp-hour rating, but in the case of Lead Acid battery, it is Amp hour. We will describe this in later section.
Working of Lead Acid Battery
Working of the Lead Acid battery is all about chemistry and it is very interesting to know about it. There are huge chemical process is involved in Lead Acid battery’s charging and discharging condition. The diluted sulfuric acid H2SO4 molecules break into two parts when the acid dissolves. It will create positive ions 2H+ and negative ions SO4-. As we told before, two electrodes are connected as plates, Anode and Cathode. Anode catches the negative ions and cathode attracts the positive ions. This bonding in Anode and SO4- and Cathode with 2H+ interchange electrons and which is further react with the H2O or with the water (Diluted sulfuric acid, Sulfuric Acid + Water).
The battery has two states of chemical reaction, Charging and Discharging.
Lead Acid Battery Charging
As we know, to charge a battery, we need to provide a voltage greater than the terminal voltage. So to charge a 12.6V battery, 13V can be applied.
But what actually happen when we charge a Lead Acid Battery?
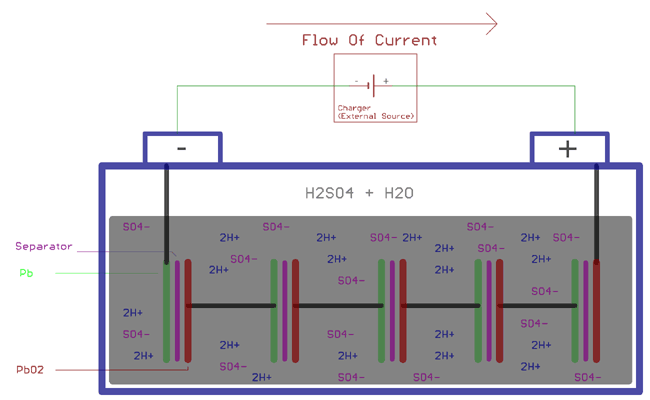
Well, the same chemical reactions which we described before. Specifically, when the battery is connected with the charger, the sulfuric acid molecules break into two ions, positive ions 2H+ and negative ions SO4-. The hydrogen exchange electrons with the cathode and become hydrogen, this hydrogen reacts with the PbSO4 in cathode and form Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) and Lead (Pb). On the other hand, SO4- exchange electrons with anode and become radical SO4. This SO4 reacts with PbSO4 of anode and create the lead peroxide PbO2 and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The energy gets stored by increasing the gravity of sulfuric acid and increasing the cell potential voltage.
As explained above, following chemical reactions takes place at Anode and Cathode during the charging process.
At cathode
PbSO4 + 2e- => Pb + SO42-
At anode
PbSO4 + 2H2O => PbO2 + SO42- + 4H- + 2e-
Combining above two equation, the overall chemical reaction will be
2PbSO4 + 2H2O => PbO2 + Pb + 2H2SO4
There are various methods applicable for charging the lead-acid battery. Each method can be used for specific lead-acid battery for specific applications. Some application uses constant voltage charging method, some application uses a constant current method, whereas tickle charging also useful in some cases. Normally battery manufacturer provides the proper method of charging the specific lead-acid batteries. Constant current charging is not typically used in Lead Acid Battery charging.
Most common charging method used in lead acid battery is constant voltage charging method which is an effective process in terms of charging time. In full charge cycle the charge voltage remains constant and the current gradually decreased with the increase of battery charge level.
Lead Acid Battery Discharging
Discharging of a lead acid battery is again involved with chemical reactions. The sulfuric acid is in the diluted form with typically 3:1 ratio with water and sulfuric acid. When the loads are connected across the plates, the sulfuric acid again breaks into positive ions 2H+ and negative ions SO4. The hydrogen ions react with the PbO2 and make PbO and water H2O. PbO start reacting with the H2SO4 and creates PbSO4 and H2O.
On the other side SO4- ions exchange electrons from Pb, creating radical SO4 which further creates PbSO4 reacting with the Pb.
As explained above, following chemical reactions takes place at Anode and Cathode during the discharging process. These reaction are exactly opposite of charging reactions:
At cathode
Pb + SO42- => PbSO4 + 2e-
At anode:
PbO2 + SO42- + 4H- + 2e- => PbSO4 + 2H2O
Combining above two equation, the overall chemical reaction will be
PbO2 + Pb + 2H2SO4 => 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
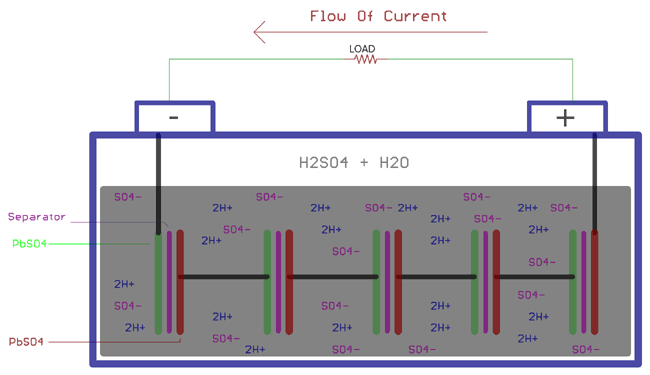
Due to the electron exchange across anode and cathode, electron balance across the plates is affected. The electrons then flow through the load and the battery gets discharged.
During this discharge, the diluted sulfuric acid gravity decrease. Also, at the same time, the potential difference of the cell decrease.
Risk Factor and Electrical Ratings
The Lead Acid battery is harmful if not maintained safely. As the battery generates Hydrogen gas during the chemical process, it is highly dangerous if not used in the ventilated area. Also, inaccurate charging severely damages the battery.
What are the standard ratings of Lead Acid battery?
Every lead-acid battery is provided with datasheet for standard charge current and discharges current. Typically a 12V lead-acid battery which is applicable for the automotive application could be ranged from 100Ah to 350Ah. This rating is defined as the discharge rating with an 8 hour timing period.
For example, a 160Ah battery could provide 20A of supply current to the load for 8 hours of the span. We can draw more current but it is not advisable to do so. By drawing more current than the maximum discharge current in respect of 8 hours will damage the battery efficiency and the battery internal resistance could also be changed, which further increases the battery temperature.
On the other hand, during the charging phase, we should be careful about the charger polarity, it should be properly connected with the battery polarity. Reverse polarity is dangerous for the lead-acid battery charging. The readymade charger comes with a charging voltage and charging current meter with a control option. We should provide greater voltage than the battery voltage to charge the battery. Maximum charge current should be the same as the maximum supply current at 8 hours discharging rates. If we take the same 12V 160Ah example, then the maximum supply current is 20A, so the maximum safe charging current is the 20A.
We should not increase or provide large charging current as this will result in heat and increased gas generation.
Lead-acid battery maintenance rules
- Watering is the most neglected maintenance feature of flooded lead-acid batteries. As overcharging decreases water, we need to check it frequently. Less water creates oxidation in plates and decreases the lifespan of the battery. Add distilled or ionized water when needed.
- Check for the vents, they need to be perfected with rubber caps, often the rubber caps sticks with the holes too tightly.
- Recharge lead-acid batteries after each use. A long period without recharging provides sulfating in the plates.
- Do not freeze the battery or charge it more than 49-degree centigrade. In cold ambient batteries need to be fully charged as fully charge batteries safer than the empty batteries in respect of freezing.
- Do not deep discharge the battery less than 1.7V per cell.
- To store a lead acid battery, it needs to be completely charged then the electrolyte needs to be drained. Then the battery will become dry and can be stored for a long time period.





